Supplements: Your Guide
“Can we improve egg quality?”
“Can we improve egg quality?”
In all honesty I believe that although there is nothing you can do about the numbers or the genetic make-up of your eggs, there is a lot you can do to improve the environment your eggs are developing in.
Doctors and scientists all agree that eggs can be aged by free radical damage, endocrine disrupting chemicals and poor lifestyle choices, especially smoking.
“Every day, our bodies comes into contact with fertility-harming substances called reactive oxygen species—ROS for short. ROS are also called free radicals. It’s normal for your body to make some free radicals. And in some cases free radicals are important for normal physiological processes. For example, free radicals are needed during ovulation. But, excess free radicals lead to a condition called oxidative stress, which negatively impacts both female and male fertility”
Factors Contributing to Oxidative Stress
Here are just some of the things that can cause your free radical levels to skyrocket:
Toxins such as bisphenol-A (BPA), parabens, phthalates, herbicides and pesticides
Ageing
Psychological stress
Obesity
Poor nutrition
Not enough exercise
Drinking excess caffeine
Increased temperature in a man’s scrotum
Imbalanced insulin levels due to sugar intake, diabetes or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Using a cell phone or other technology or placing it near reproductive organs
Enter the role of antioxidant supplements to help combat this oxidative stress and increase fertility.
CoQ10
The antioxidant CoQ10 may help improve egg quality in women over 35. CoQ10 is an essential catalyst for the creation of energy at the cellular level. It works within the mitochondria to support energy production. CoQ10 levels are highest during our first 20 years of life with its production decreasing with age. As a result, older eggs are far less efficient in energy production. Ovulation is an extensive process that requires an immense amount of energy. Oocytes depend on CoQ10 for the energy required for this process. Low levels of CoQ10 can result in decreased energy production and increased oxidative stress, each of which can impact ovulation. By supplementing with CoQ10, women may be able to improve egg quality.
DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone)
DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) is a powerful hormone that acts as a precursor to testosterone and estrogen. It’s a natural steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands. DHEA peaks in our 20’s and then declines as we get older. Recent studies show that DHEA may help increase follicular stimulation and estrogen production in women.
How does DHEA work?
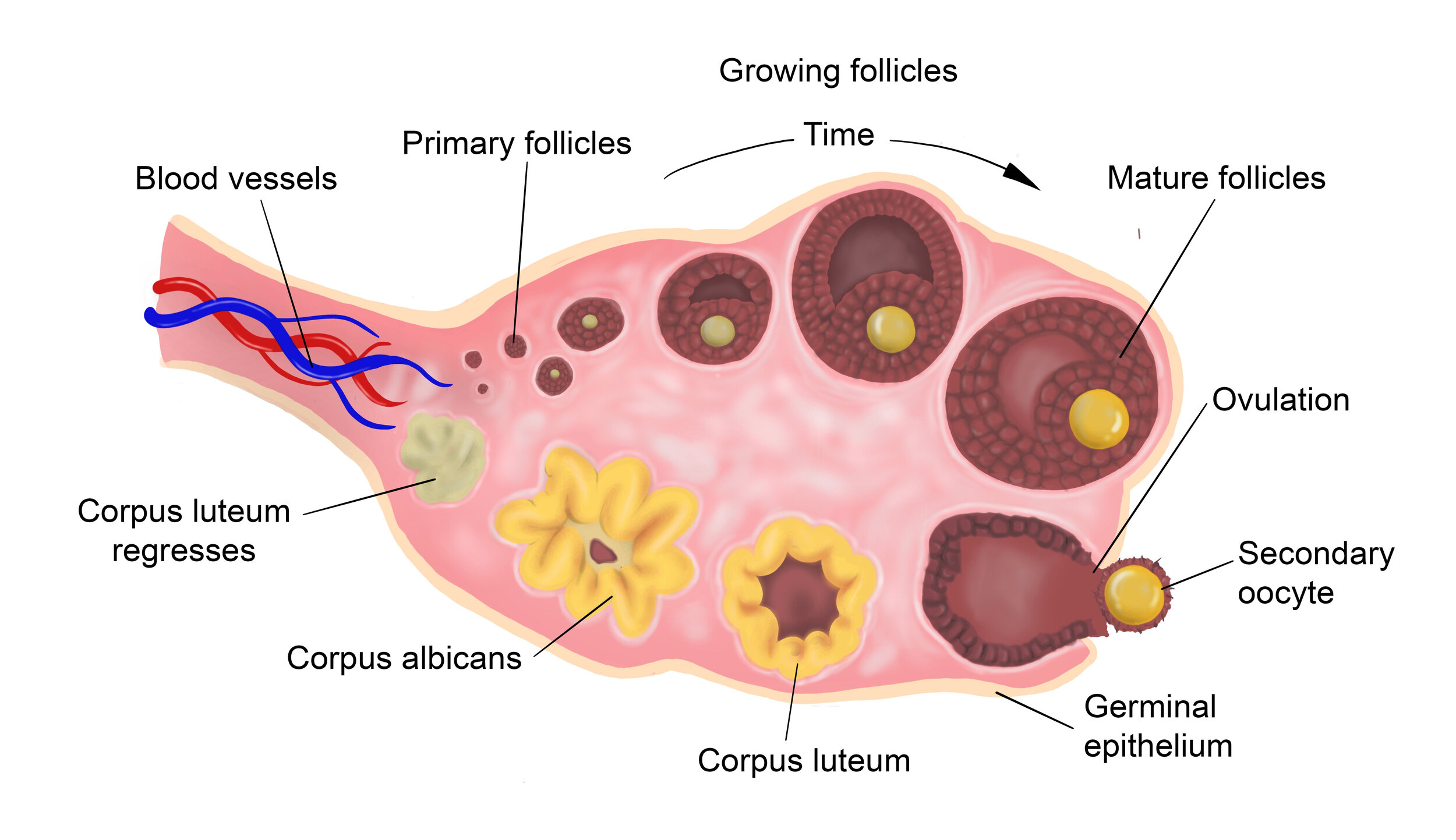
It’s thought to stimulate granulosa cells, the cells surrounding each growing follicle (egg), increasing the numbers of follicles and therefore eggs.
Since DHEA production declines with age, taking a supplement may help improve egg quality for women diagnosed with
Decreased Ovarian Reserve (DOR) or
Premature Ovarian Failure (POF).
Please note that DHEA should not be taken in high doses due to its potential side effects. As it is a male hormone women may experience androgenizing side effects including acne, increased facial hair and hair loss. Long term side effects are unknown but there are concerns about increased risk of hormone sensitive cancers such as breast cancer.
Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone and a strong antioxidant that can support cellular health. In addition to promoting sleep, melatonin acts in several ways to help the reproductive cycle:
a) as an antioxidant within the egg cell, improving egg quality
b) as a signalling molecule in the brain, controlling reproductive hormone rhythm and
c) protects the embryo and facilitates implantation. Controlled melatonin supplementation is able to protect an immature egg, particularly during ovulation, from oxidative stress. It is also involved in egg maturation and embryo development.
L-Arginine
L-Arginine is an amino acid that may help improve ovarian response. Supplementing with L-Arginine can help increase blood circulation to the uterus and ovaries, thus creating an optimal environment for egg production and implantation of a fertilized egg.
Inositol
Inositol, in the form of myo-inositol, may help improve fertility rates in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Inositol has been shown to help modulate the presence of insulin in the body, which may have significant effect on ovulation. This helps improve glucose metabolism in women with PCOS. Clinical studies have demonstrated that Inositol can help restore normal ovulation, improve egg quality and increase fertilization rates in women with PCOS.
Glutathione
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant and detoxifier. Egg quality is dependent on Glutathione due to its free-radical fighting abilities. Yes to this! Oxidative stress can result in an increase in hormone levels and impair ovarian health. Glutathione helps protect eggs from damage throughout their extensive development process.
Have a question for us? Feel free to contact us. Alternatively, you can find us on Instagram @thefertilitytalk